Welcome to the NLP Newsletter! The third issue covers topics such as improving conversational agents, releases of language-specific BERT models, free datasets, releases of deep learning libraries, and much more.
Don’t forget to subscribe to the publication or follow us on Twitter 🐦 to get the latest of the NLP Newsletter and dair.ai.
Publications 📙
Language-specific BERT models
I have lost count of how many language-specific BERT models there are now but here a couple of the recent releases:
- Dutch BERT (RobBERT, BERTje)
- German BERT
- Portuguese BERT
- French BERT (CamemBERT, FlauBERT)
- Italian BERT (AlBERTo, UmBERTo)
- Spanish BERT (BETO)
- Arabic BERT (araBERT)
Note that most of these models are also being made available through the Hugging Face’s Transformer library, which was recently upgraded to 2.4.1.
Overly Optimistic Prediction Results on Imbalanced Data: Flaws and Benefits of Applying Over-sampling
This paper reveals and extensively discusses some of the flaws and benefits of applying over-sampling to deal with imbalanced datasets before partitioning the datasets. Furthermore, the work reproduces previous studies and identifies this methodological flaw that produces overly optimistic results.
Encode, Tag and Realize: A Controllable and Efficient Approach for Text Generation
In an effort to reduce the effect of hallucination (producing outputs not supported by input text) common in seq2seq-based text generation methods, a group of Google engineers open-sourced a method for text generation called LaserTagger. The main idea of the method is to produce outputs by tagging words with predicted edit operations (e.g., KEEP, DELETE-ADD, etc.) and applying it to the input words in a so-called realization step. This replaces the common text generation method that just generates output from scratch which is generally slow and error-prone. The model offers other benefits besides generating fewer errors, such as enabling the parallel predictions of edit operations while still maintaining good accuracy and outperforming a BERT baseline in scenarios with a smaller number of training examples.
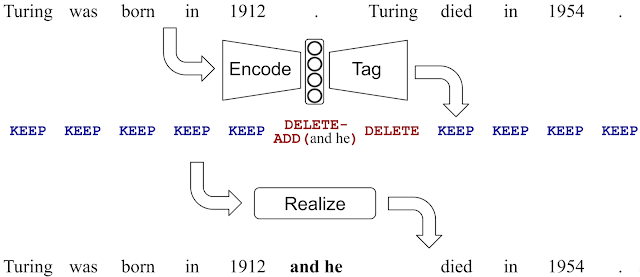
“LaserTagger applied to sentence fusion. The predicted edit operations correspond to deleting “. Turing” and adding “and he” before it. Notice the high overlap between the input and output text.” — source
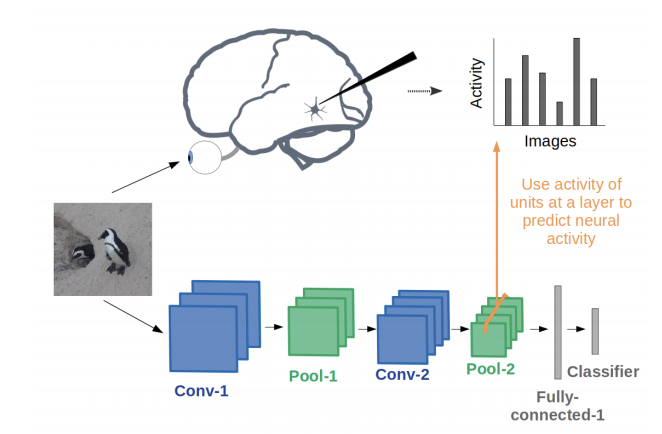
Convolutional Neural Networks as a Model of the Visual System: Past, Present, and Future
Grace Lindsay released this nice and easy-to-read report on the history of CNNs and how they are evaluated as models of biological vision, i.e., how do CNN representations compare to those of the brain? The discussion of the emerging opportunities on the use of CNNs for vision research is highly recommended for readers.
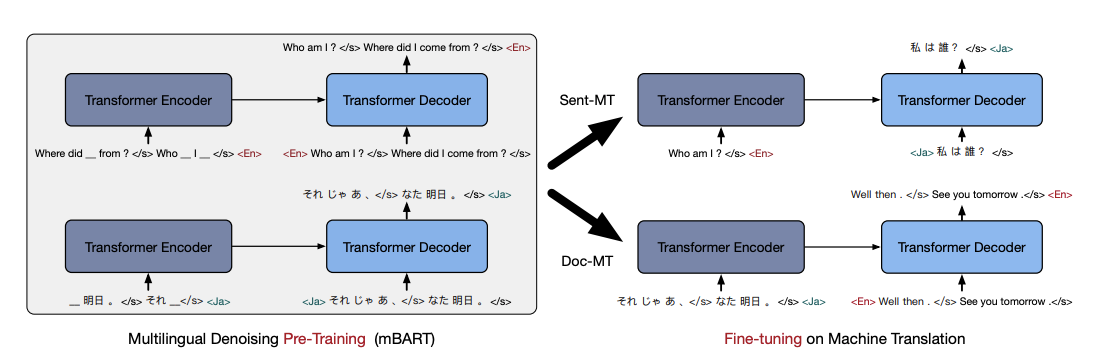
Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation
Facebook AI published mBART a method based on a multilingual seq2seq denoising auto-encoder pretrained on large-scale monolingual corpora for machine translation across 25 languages. This work follows the pretraining scheme of Lewis et al., 2019, BART, and investigates the effects of denoising pretraining on multiple languages such as Korean, Japanese, and Turkish, among other languages. Input text involves the masking of phrases and permuting sentences (noising). A Transformer-based model is learned to reconstruct the text across many languages. The complete autoregressive model is trained only once and can be fine-tuned on any of the language pairs without involving any task-specific or language-specific modifications. Both document-level and sentence-level translation problems are approached. Besides showing performance gains, the authors claim that the method works well on low-resource machine translation.
On improving conversational agents
Meena is a neural conversational agent that aims to conduct improved conversations that are more sensible and specific — metrics that are defined to capture important attributes from a human conversation (e.g., fluency). The model learns the conversation context via an encoder and formulates a sensible response via the decoder. It is reported that improvement in the quality of conversations was possible by considering more powerful decoders.
You can also catch Alan Nichol’s (Co-Founder of Rasa HQ) thoughts on this work.
Creativity and Society 🎨
ML tools — reading comprehension test and sentiment analyzer
Ming Cheuk built this fun app that allows you to test the reading comprehension capabilities of a model trained on deep learning methods, in particular, using Google AI’s language model called ALBERT. ALBERT is a tiny version of BERT for learning language representations. The author explains more about the project and approaches used in this blog post.
Hendrik Strobelt also released a small project where he shows how to prototype an interactive sentiment analyzer. These are all projects that help to highlight some of the great ideas coming from ML and NLP. If you have a serious and interesting project you are working on, please reach out and we can feature it in the publication/newsletter.

The journey of a self-taught AI researcher at Google
In this candid interview, you can hear directly from Emil, an ML researcher at Google Art & Culture, about his journey in the pursuit of a career in AI as a self-taught researcher.
Tools and Datasets ⚙️
Free Datasets
Google Dataset Search is officially out of beta and now provides up to 25 million datasets to search upon. If you ever want inspiration for your next data science or machine learning project, this is the place to find references to datasets hosted all over the internet. It’s basically a search engine for datasets, this is amazing work and required tremendous effort!
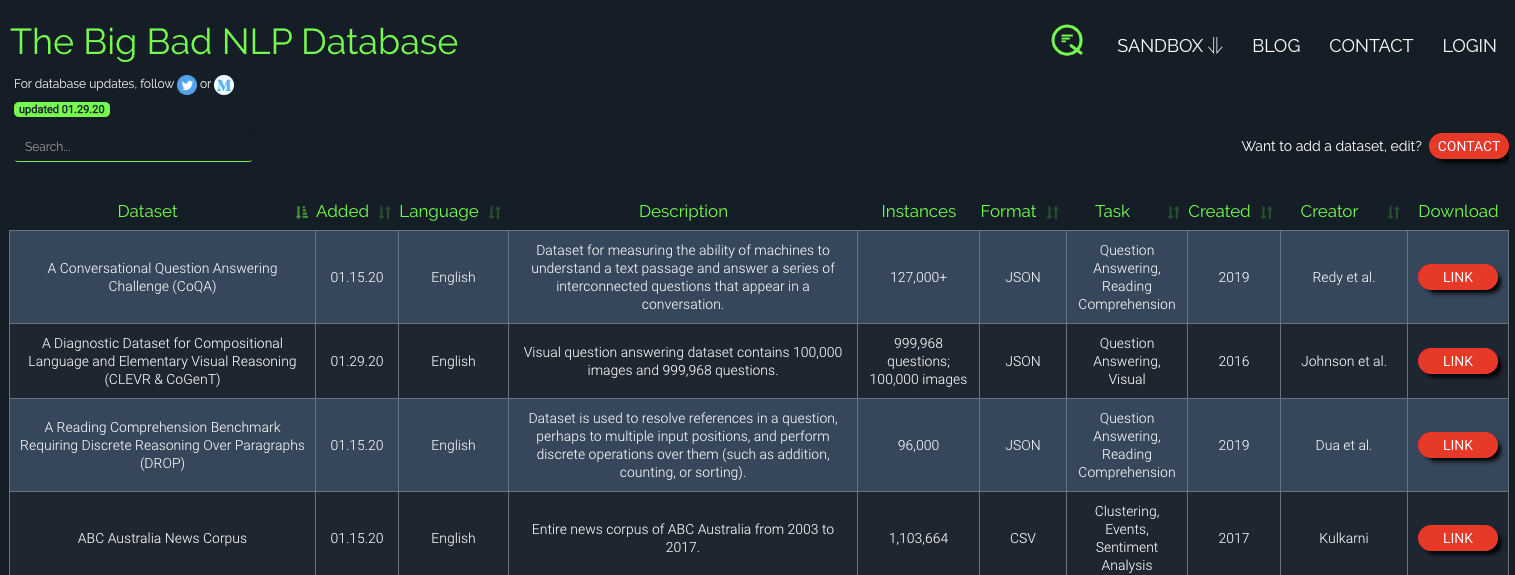
The Big Bad NLP Database is a website where you can search a dedicated database of over 200 NLP datasets of all types for tasks such as commonsense, sentiment analysis, questions answering, entailment inference, among others.
Reinforcement learning library
There are several good reinforcement libraries out there. Recently, Chris Nota developed and released a PyTorch library for building reinforcement learning agents based on popular deep RL algorithms such as DQN, PPO, and DDPG, among others. The emphasis of the library is on object-oriented design and for enabling the quick implementation and evaluation of novel reinforcement learning agents.
ML Explainability and Interpretability
If you are currently working with text-based language models and want to understand how to interpret them more easily when applied to different language tasks, then you may be interested in Captum. Captum is an interpretability library that can be used to analyze feature importance, interpreting text and vision models, interpreting multimodal models, and other models such as BERT used for question answering.
If you are interested in model explainability, this set of tutorials may also interest you. It includes methods for understanding feature importance via notebooks.
Machine learning and deep learning libraries
The Google Research team released Flax — a flexible and powerful neural network library based on JAX which provides a framework for fast computing and training machine learning models using the typical Numpy APIs.

Flax syntax
Thinc is a lightweight deep learning library developed by the makers of spaCy. It offers functional-programming APIs for composing, configuring, and deploying custom models built with libraries like PyTorch and TensorFlow.
Lyft releases Flyte which is a multi-tenant, production-ready, and serverless platform for deploying concurrent, scalable, and maintainable ML and data processing workflows.
A tool for conversational AI
The open-source conversational AI framework DeepPavlov offers a free and easy-to-use solution for building dialogue systems and complex conversational systems. DeepPavlov comes with several predefined components for solving NLP-related problems. It integrates BERT (including conversational BERT) into three downstream tasks: text classification, named entity recognition (and sequence tagging in general), and question answering. As a result, it achieved substantial improvements in all these tasks. (Google Colab | Blog | Demo)
Ethics in AI 🚨
Facial recognition and privacy
The New York Times wrote an interesting report on different perspectives of privacy as it relates to facial recognition technology. The focus of this story is around a “secretive company” called Clearview which allegedly uses AI technology to build universal facial recognition using images scraped from social media sites such as Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube, among others. The said technology raises concerns about privacy but it is also claimed to be used mostly for law enforcement. Read more of the story here.
Human-Level AI Progress
In this report, Jeremy Kahn extensively discusses the difference between “Narrow AI” and “General AI” in the context of the current progress of AI technology. Besides the many topics discussed, lots of questions arise on the returns of (if ever possible) achieving AGI. The report also mentions the recent interest of big tech companies investing in these efforts. Most notably, the report includes several concerns raised by respected researchers claiming the “irresponsible and unethical” behavior displayed by some research organizations that try to manipulate AI narratives for their benefit.
Privacy-preserving AI technologies
I am a strong believer in ethical and responsible AI, it’s not a fad nor is it the time to downplay it, it’s a serious endeavor that requires the best of minds to get it right. One of the biggest efforts I have witnessed in this aspect of AI is the privacy-persevering efforts from OpenMined, a community that aims to build more responsible AI tools with privacy as a first-class citizen. If you want to know more, listen to Andrew Trask, lead of this effort, talk more about this initiative in this recording that is part of the MIT Deep Learning lecture series.
Understanding AI Ethics and Safety
Dr. David Leslie published this very detailed report on topics that help to better understand AI in the context of ethic and safety. It aims to help developers and researchers better design and implement AI systems for the public sector.

Articles and Blog posts ✍️
Speeding up tokenization tutorial
Steven van de Graaf wrote this article reporting performance gains when using Hugging Face’s new Tokenizers library as compared to the standard, built-in tokenizer used in Transformers. Steven reports 9x speed-up and an implementation that takes 10.6 seconds to tokenize 1 million sentences.
Can language models really comprehend?
The Gradient recently featured this post by Gary Marcus where he discusses what he believes are fundamental flaws behind language models like GPT-2. The main argument of Gary Marcus is that a model that is trained to be able to predict the next word is not necessarily a model that could understand or reason, i.e., “Prediction is a component of comprehension, not the whole thing.” He also discusses the importance of innateness in the context of language and argues that the current language models don’t consider it.
Curriculum for Reinforcement Learning
Can designing curriculum-based methods help an RL agent to learn? Lillian Weng summarizes several curriculum-based approaches and how they can be leveraged to train effective reinforcement learning agents. Weng discusses the challenges of designing an efficient curriculum learning approach which generally requires sorting complexity of tasks and providing the model a sequence of tasks that increase in the level of difficulty during training.
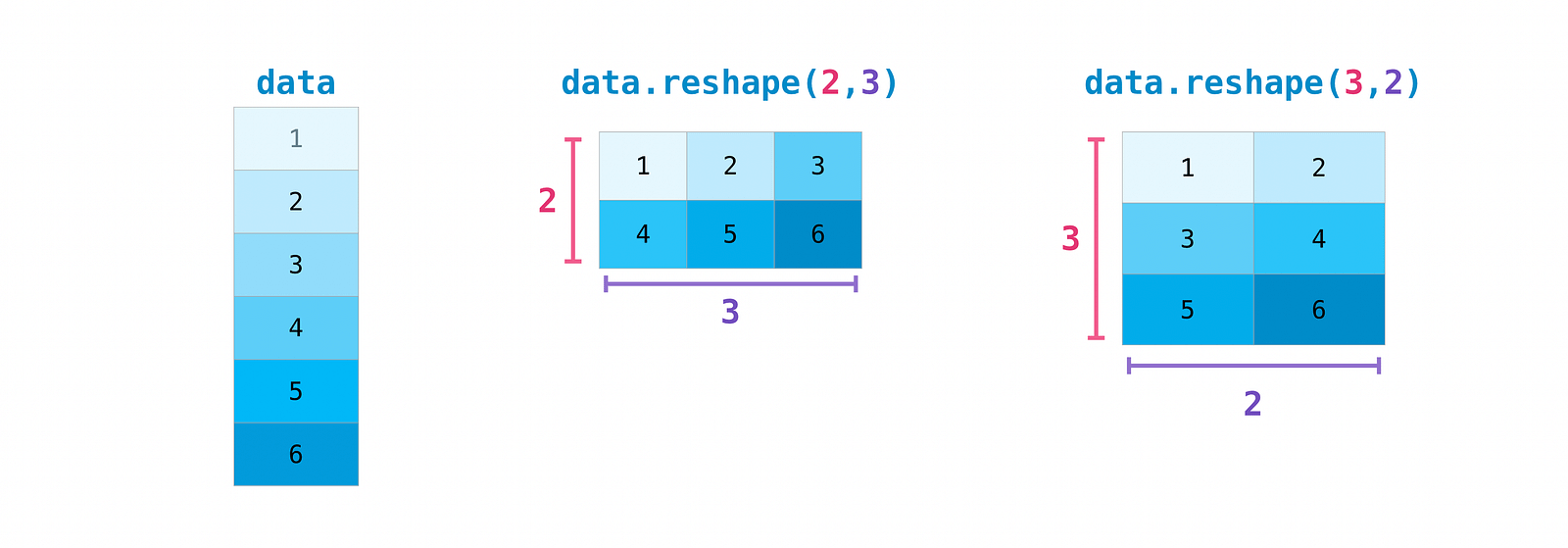
Introduction to NumPy
I always recommend anyone that is getting started with machine learning to get plenty of practice with NumPy. A lot of the high-level libraries used for deep learning and machine learning today use NumPy APIs in some way so it’s a very important tool to understand internally. Anne Bonner recently released this very detailed tutorial introducing the basics of NumPy.
Education 🎓
Foundations of machine learning and statistical inference
Anima Anandkumar, from Caltech, released a course titled “Foundations of machine learning and statistical inference”. The course focuses on ML concepts such as matrices, tensors, optimization, probabilistic models, neural networks and much more. This is a great course because it focuses on the theoretical aspect of ML, which is just as essential to understand and improve more advanced methods. (video playlist | course syllabus)
Deep Learning Lecture Series
DeepMind partnered with UCL to release the Deep Learning Lecture series, which includes 12 lectures that will be delivered by leading research scientists at DeepMind. Topics include how to train a neural network using methods such as attention, memory, and generative modeling, and much more.
~7 million syllabi
Education is a vital part of growing communities and entire industries. It is where the seed of innovation is planted. Open Syllabus is a non-profit organization that is using the power of crowdsourcing to map the curriculum of higher education into one free-for-all online database. It currently contains roughly seven million syllabi.
Discussing, Sharing, and Learning about ML
r/ResearchML is a new machine learning subreddit for discussing ML papers. This one is more focused on research and encouraging deeper discussions.
practicalAI is a website where you can explore and discover ML topics curated by the community and experts.

Notable Mentions ⭐️
Learn more about how GitHub is leveraging machine learning to spot easy and personalized issues for developers so that they can tackle issues that are aligned with their interests. This encourages quicker and more contributions from open-source contributors.
Catch up with the latest top NLP news on the recent issue of the NLP News by Sebastian Ruder. Highlights include an update of NLP Progress, retrospectives of the past decade, new NLP courses, among other topics.
Check out this incredible list of TensorFlow 2.0 deep learning notebooks that range from CycleGAN to Transformers to image captioning tasks. They were publicly released by the Deep Learning for Science School at LBNL.
An impressive and easy to follow blog post explaining the basics of Bayesian neural networks. A great introduction for starters.
John Schulman shares some advice for upcoming ML researchers on how to better choose research problems and be more strategic about implementing and tackling the research tasks at hand. John also shares tips for personal development and continual progress.
Editor’s note: Thanks for all the love ❤️ and support 🤗 you have been giving to the newsletter and this publication. It helps to remind me of how important this effort is and why I should always take the time to distill the best of ML and NLP that’s happening more recently. If you would love to contribute 💪, please feel free to reach out. Suggestions are highly welcome, this is a community effort as I see it. Also, the official website of dair.ai is ready! I will make the official announcement here in an upcoming post. The website aims to simplify and extend the reach to readers from all over the world 🌐.
